Fill This Form To Receive Instant Help
Fill This Form To Receive Instant Help
Homework answers / question archive / Aggieland Distributing had current assets of $700, Inventory of $300, long-term assets of $1,500, current liabilities of long-term liabilities of $1,000, and shareholder's equity of $800
Aggieland Distributing had current assets of $700, Inventory of $300, long-term assets of $1,500, current liabilities of long-term liabilities of $1,000, and shareholder's equity of $800. The current ratio (rounded) is: 6 a. 1.50 b. 1.75 c. 0.34 d. 2.00 e. 1.33 a. 3. Which of the following could possibly be the quick ratio? 6 1.00 b. 1.80 c. 2.00 d. 2.50 e. 3.50 4. Tommy Joe, owner of Nettles Construction Supply, is reviewing the latest set of financial statements for his company. Tommy Joe is confused by some of the data. Last year the current ratio was 2.50. This year it is down to 1.85. However, the quick ratio was 1.05 last year and up to 1.50 this year. Which of the following best explains how the current ratio can decrease at the same time that the quick ratio increases. 1 a. Tommy Joe is obviously not calculating something correctly b. If inventory decreases, the current ratio can decrease without impacting the quick ratio. c. Inventory has obviously increased. d. If inventory increases, the quick ratio will be more impacted since inventory is subtracted from current assets in the calculation, e. None of the above offer an explanation

Solution
2. Current assets = $700
Long term assets = $1,500
Long term liabilities = $1,000
Shareholders equity = $800
We have the equation:
Equity + Liabilities = Assets
More pertinent to the problem:
Shareholders Equity + Long term Liabilities + Current Liabilities = Long term assets + Current assets
Replacing the values we have in the above equation:
$800 + $1,000 + Current Liabilities = $1,500 + $700
$1800 + Current Liabilities = $2200
Current Liabilities = $2200 - $1800
Current Liabilities = $400
Current ratio = Current Assets 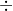 Current liabilities
Current liabilities
Current ratio = 700 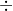 400
400
Current ratio =1.75
3. Quick assets are highly liquid assets that consist of cash or cash-like liquid assets that can be converted immediatly into cash in order to repay the current liabilities. Inventory is not considered highly liquid and hence is to be excluded from the current assets to find quick assets.
Quick assets = Current assets - Inventory
Value of inventory provided is $300
So Quick assets = 700 - 300
Quick assets = $400
Quick ratio = Quick assets 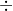 Current liabilities
Current liabilities
Quick ratio = $400 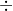 $400
$400
Quick ratio = 1
4. Current ratio was 2.50 last year but now down to 1.85
Quick ratio was 1.05 last year but it is now up at 1.50
The most common current asset that is not highly liquid in most businesses is inventory. A significant change in the inventory levels alone can cause a significant change in the current and quick ratios.
Last year the inventory to current liability ratio was 2.50 - 1.05 = 1.45 (Current ratio - Quick ratio)
(Since current assets were $2.50 to every $1 of current liability and quick assets were $1.05 to every $1 of current liability (both have a common denominator), the difference represents the inventory value per dollar of current liability of that year)
This year the inventory to current liability ratio is 1.85 - 1.50 = 0.35
So the inventory levels have come down in relation to the current liabilities from $1.45 to $0.35 per dollar of current liability.
A big decline in inventory levels under normal circumstances would mean conversion of inventory at a faster rate into cash / highly liquid assets during the year which has increased the cash and cash equivalent or highly liquid assets drastically thereby increasing the quick ratio. However, if inventory is under abnormal circumstances destroyed by fire or spoilage without any insurance or lets say, large portions are given out for free (higly improbable!) the liquid assets would not change much and so the quick ratio may not be affected.
So the best explanation is alternative b. If inventory decreases, the current ratio can decrease without impacting the quick ratio.

